With all the press about lead paint in toys, industrial chemicals in food, and items made in China, it’s clear that with the low cost of China-made goods comes a great challenge in quality management.
First, let me start this post with a few personal perspectives on recent events. I think an important perspective to keep in mind is “Hanlon’s Razor”, somewhat paraphrased here: Never attribute to malice that which can be adequately explained by ignorance. Actually, I just read the Wikipedia entry for it, and there’s a nice pithy version the Brits have: “Cock-up before conspiracy”. While it is true that some people are out there to make a buck at any cost, I think the majority of the mistakes are made out of ignorance. Most of the rank-and-file in factories don’t know what their product is ultimately used for, yet are under intense pressure to reduce costs, so bad decisions get made. I have also seen situations where products are either woefully underspecified, or customers overwhelm the factory with all kinds of frivolous requirements, most of which the customer doesn’t follow up on. In the end, the factories play this game of “ship and find out” — if the customer doesn’t notice a spec was missed, then the spec must not have been important. It’s not a great game to be playing, and it means that companies need to be ever vigilant about audits and keeping the quality standard up.
So one fundamental problem is that many of the Chinese do not understand or appreciate basic things that we take for granted in America, and vice versa. Many of the workers, while well educated in the fundamentals, did not grow up in a “gadget culture” like we have in the US, so you can’t assume anything about their subjective abilities to interpret specifications for a product. For example, you can tell a US engineer “I’d like a button on that panel”, and you’ll probably get something back pretty close to what you expected in terms of look and feel, since you and the engineer share a lot of common experiences and expectations for a button on a panel. However, if you did the same in China, you’ll probably get something that looks a little awkward, performs a little klunky, but is darn cheap and is really easy to build and test (which isn’t a bad thing, but Americans gadget connoisseurs just won’t buy something that looks awkward and has klunky performance).
Which brings me to my next point: ultimately it’s the consumers who want — nay, demand — low priced goods that drives the decision to go to China. And the trouble is that aside from the label on the product that says “Made in China” or “Made in the USA”, consumers really don’t care about the manufacturing process that went into it. What markup would you pay for a gadget that said made in the USA on it? The cost premium for labor is over 10x between the US and China — think about it. Can the average US factory worker be 10x more productive than the average Chinese factory worker? It’s a hard multiplier to play against. I’m not saying there is no value in domestic vendors: it would be a lot less effort and less risk for me to get stuff made in the US. In fact, most of the early prototypes are made in the US because of the enormous value that the domestic vendors can add. However, the pricing just doesn’t work out for a mass-market product. Nobody would buy it because its price wouldn’t justify its feature set. One could even accuse me of being lazy if I were to just stick with a domestic vendor and pawn the cost off onto the customers.
Back to the topic of the Challenge of Quality. In the end, there is no substitute for going out to China and getting directly involved in the quality process. I suspect that the toy manufacturers and food manufacturers don’t fly technicians out to factories in China to oversee things on a regular basis. Contrast that with what Apple does — they send out a cadre of engineers that work intense two-week shifts in the factories (well, Foxconn typically — affectionately nicknamed “Mordor” by some). I bumped into them frequently at the expat bars in Shenzhen. Western-style management and quality control based in China is one of the important services that PCH China Solutions offers us. If we have a problem with a vendor, PCH sends a guy to their factory right away to see what’s going on — no phone tag, no fedex filibuster. Factory owners in China tend to be very responsive when you show up at their doorstep.
Thus, Chumby’s approach to the quality conundrum is a holistic one. We started by having an engineer (me) out there almost on day one to survey the situation at the factory. It’s important to learn what the factory can and cannot do. You look at what’s being built on the line, and the techniques used. Then, when it comes time to engineer the product, you try to use the processes and techniques that are most comfortable for the factory. When you must do something new — and any good, innovative product will need to do this — you pick your battles and you focus on them, because anything new you try will be a multi-week challenge to get right. This applies to even the smallest detail; if the factory shrink-wraps goods in plastic, and you want to wrap it in paper, then plan on spending a lot of focus developing the paper-wrapping process, because it’s quite possible that none of the line workers there have even seen a paper-wrapped product before.
Of course, the preferred approach to developing a process is to be in the factory. There’s nothing like standing on the line and showing the workers who will be building the device how it should be done. Below is a video of me training the line on how to attach a piece of copper tape to the LCD assembly to form a proper EMI shield.
Typically, when you are able to demonstrate a process in this detail and intimacy, they will get it right within hours. This is part of the reason why I have spent so much time in China the past few months.
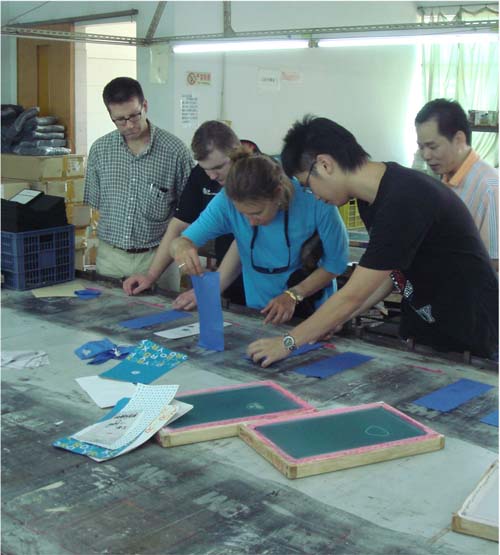

Above is a photo of Steve Tomlin (Chumby’s CEO) and Susan Kare (our Artistic Director) at the sewing factory working out the details of logo silkscreening. <shameless plug>Everyone gets involved in the quality process at Chumby!</shameless plug>
However, it’s not always possible for us to send someone out there — I for one like to be here in the US, and so does my girlfriend — so we rely a lot on PCH to watch the quality and make sure things go well. The Irish guy in the video below is Joe from PCH, and he’s reviewing the process for assembling the chumby bag with the line manager in one of our factories.
Often times, due to the challenges of working long distance, new processes will take weeks to phase in if you aren’t there to tweak and approve on the spot, because every single tweak involves almost a round-trip through fedex. Now that I’ve been through this a few times, as a rule of thumb I allocate two weeks per tweak, as opposed to the few hours it takes when you’re out there.
You can see how that adds up fast.
Given the difficulty of overseeing operations oversees, a strategic capability to have in place is remote electronic monitoring of the products’ test results. I developed for chumby a set of testers that programs, personalizes, boots, verifies and measures every device. All of the data from the process is recorded to a log, and at the end of the day, the log is transferred to a server in the US. From this data you can debug a plethora of problems on the floor. I can tell if an operator at a particular tester is having trouble with their barcode scanner, for example; or, I can tell immediately if there is a yield problem that day, or if the throughput is slower than expected. It’s very powerful to have this home-grown audit capability in place, because the factory knows you are watching them. In fact, having such a capability in place can make relationships with the factory run better because the factory eats the cost of yield problems (at least initially) — so they appreciate it when the design engineer can offer expedient advice and help before any problems get out of hand.

A pair of chumby test stations in the factory in China. If you ever meet me in person, ask me about those laptops. There’s quite a story behind the trouble we went through getting them into China.
Finally, once everything is set up, things can run autonomously at the factory. At our PCB factory, the first pass of final inspection is done manually — a set of human eyes go over every circuit board, and then with the help of a cardboard template, another operator ensures that no components are missing. The units then go on to automated testing.
No, those aren’t children working on the line. If you think they are, go guess an Asian woman’s age. She’ll be flattered — or annoyed that she’s still being carded at the bar.
Periodically, both PCH and the factory perform RoHS (a hazardous chemical safety standard required in Europe, but ironically not in the US) spot testing on the units to ensure that there is no contamination with a specified set of potentially harmful chemicals, including lead. This is done routinely on all products, even those only shipping to the US, because the latent contamination on the line could prevent other products manufactured on the same line from shipping to Europe.
It’s also important for Chumby in the US to continue to sample units for QC purposes. To this end, we order devices regularly and characterize them, and then dissect them to ensure that all the operating procedures are being followed.
Despite all these safeguards, you have to expect some mistakes to be made. Every product goes through an initial phase where all the bugs that weren’t caught by internal QA get pounded out. You have to rely on a top-notch customer service and support team and you have to plan on being very agile and innovative during this time to solve these problems and prevent them from ever happening again. If your chumby has hardware problems, you might get a call from me — I want to know what went wrong, and fix it so the problem never happens again, to you or to anyone else! What I really hope never happens is what happened to Microsoft and the Xbox360 red ring of death. This is a problem that exhibited itself only after years of use in the field, after millions of units have been shipped. These are the things that a product engineer’s worst nightmares are made of. So you see, getting the chumby to the point where we’re shipping is just the beginning. The real challenge starts now.
Wish me luck!